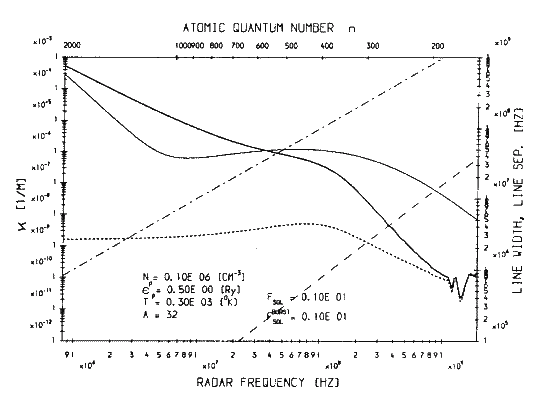
Research Fig.8c:
Theoretical ionospheric scattering coefficient (left ordinate) due to highly excited atomic states for an enhanced solar radio flux as appropriate
for a strong ('Type IV') solar burst (corresponding to the level population in
FIG.8a, i.e. for a plasma density of N
p=10
5cm
-3) for radio waves with frequencies from 820 KHz to 1.9 GHz .
A comparison to the normal solar flux case (
FIG.7a) shows that the scattering coefficient is significantly reduced for frequencies less than about 200 Mhz, with the differences increasing for lower frequencies due to the higher contribution of states affected by the photoionization; the relative importance of the latter and therefore also the effects of the solar burst on the scattering coefficient decrease with increasing plasma density (and reverse).